Tuesday, 27 June 2023
Clock and Calendar based reasoning questions for ssc,bank,ibps,rrb,ntpc and other government exams
Sunday, 25 June 2023
Ordering Test Questions for Competitive Exams
Ordering Test
The arrangement of haphazard things in a particular or definite order is called as the ordering. These things may be arranged on the basis of their size, age or characteristic etc. Questions concerning following parts may be asked in this test- . . .
1. Position series
2. Height series
3. Age series
4. Circular series
5. Line series
6. Square series
Position series
In these . questions, . the
position of· some persons from up or down or from left or right is given and
then the total no. of persons is asked. The vice - versa of this . is also
possible. Some important formulae for these type of questions-
Formula 1
Total no of persons =[Position of
person from upward + position of person from downward ]- 1
Or
Total no of persons =[Position of
person from right +position of person from left]- 1
Formula 2
Position of person from upward= [Total
no of persons- position of person from
down] +1
Or
Position of person from right= [Total
no of persons- position of person from left]
+1
Formula 3
Position of person from downward=
[Total no of persons- position of person
from up] +1
Position of person from left = [Total
no of persons- position of person from right]
+1
Formula 4
If two persons are on a definite
position from left and right and they interchange their Positions then one of them moves some
positions ahead in his own direction then-
I. Total number of persons =[First
position of first person + Second position of second person ]-1
II. Second position of first person
or second position of second person
Or
=[difference of two positions of first person]-[first
position of second person ]
Formula 1 :Example
The position of Jitendra from
upwards is 27th and from downwards is 23rd in the class. What is the total no.
of students in the class?
(A) 50
(B) 48
(C) 47
(D) 49
(E) None of these
Total number of students in class=
[ Position of Jitendra from up + Position
of Jithendra from down ] = (27 + 23) - I = 50-1 = 49
Formula 2:Example
Total no. of students in the
class of Deepu is 10. Among them the position of Deepu from downward is 4 then what is his position from upward ?
(B) 6
(C) 5
(D) 9
(E) None of these
Answer with Explanation-(A)
Position of Deepu from upward= [Total no of persons- position of person from down] +1
=[10-4]+1=7
(A) 4
(B) 3
(C) 5
(D) 2
(E) None of these
Answer with Explanation-(A)
Placement of Deepu from downward = [total no- place of Deepu from upward] +1
= [10-7]+1=4
Formula 4: Example
In a line of. girls, Shweta's position from right is 25th and Manju is on 13 th position from left. They both interchange their places. Now, Manju is on 23rd position from left. What will be the position of Shweta from right ?
(A) 36th
(B) 33rd
(C) 31st
(D) 35th
(E) None of these
Answer with Explanation-(D) Using formula (4)
Second position of first person or second position of second person
= [Difference of two positions of second person]+ [First position of first person]
Second Place of Shweta=[ Difference of two positions of Manju]+[ First position of Shweta ]
= [23-13]+ 25 = 10+25=35
Height Series Test
In these questions, a group of persons in disordered heights is given. We have to arrange them orderly and find their positions.Example 1. Ram is taller than Shyam, but not as much as Rajan. Arjun is taller than Sohan who is shorter than Shyam. Who is the shortest?
(A) Rajan
(B) Ram
(C) Arjun
(D) Shyam
(E) None of these
Answer with Explanation-(E)
Write the each statement as inequality relation
Ram is taller than Shyam, but not as much as Rajan = Rajan>Ram>Shyam
Arjun is taller than Sohan who is shorter than Shyam. Arjun>Sohan<Shyam
Combining both inequality relations Rajan>Ram>Shyam>Sohan<Arjun
From above it is clear that Sohan is shorter than every other person.
Thus, Sohan is the shortest.
Click below links to Read more ...
Saturday, 24 June 2023
Statement and Conclusion Questions With Answers
Statement and Conclusion:Tips and tricks to solve faster
Direct Conclusion
Indirect Conclusion
Monday, 19 June 2023
Methods and Tips for solving Statement and Assumptions
Statement and Assumptions Questions for Competitive Exams
In this type of questions one statement which is followed by assumptions,
is given . The candidates have to decide which of the assumptions
are implicit in the given statement. Before answering the questions, it is
necessary to understand the meaning of assumption. An assumption is something supposed or taken for
granted. The following
example will illustrate the idea clearly.
- Give answer (A) if only assumption I is implicit.
- Give answer (B) if only assumption II is implicit.
- Give answer (C) if either I or II is implicit.
- Give answer (D) if neither I nor II is implicit.
- Give answer (E) if both I and II are implicit.
Assumptions-
I. Bombay and Aurangabad are connected by aeroplane service.
II. There is no other means of going from Bombay to Aurangabad.
2.Statement-Watch XYZ T.V.; your best choice.
Assumptions-
I. Among the available T .V. programmes people will always select only one choice consistently.
II. Those who prepare programmes for 'XYZ T.V.' know what the people consider as the 'Best
Answer with Explanation (B)-From the statement it is assumed that XYZ T.V Programmes are good. so, Those who prepare programmes for 'XYZ T.V.' know what the people consider as the 'Best.
If XYZ T.V Programmes are good ,it doesn’t imply that people people will always select only one choice consistently .
So,only Statement II is implicit.
3. Statement: Unemployment allowance should be given to all unemployed Indian youth above 18 years of age.
Assumptions:
I. There are unemployed youth in India who needs monetary support.
II. The government has sufficient funds to provide allowance to all unemployed youth.
Answer with Explanation (A)- Assumption I directly follows from the statement and so is implicit. But the statement does not tell about a government policy or its current position of funds. So, II is not implicit.
4. Statement : Many people fell ill after consuming meal at a wedding reception and were rushed to the nearby govt. and private hospitals.
Assumptions :
I. The relatives of the affected people may refuse to take them to the Govt. hospitals.
II. The nearby hospitals may be able to attend to all the affected people.
Answer with Explanation (B)-Assumption II is implicit because assuming this people were rushed to nearby hospitals. Statement does’t talks about peoples attitude towards Govt.Hospitals. So, II is not implicit.
Tips for solving Statement and Assumption Questions.
While Solving statement and Assumption questions ,keep in mind the following points.1. Assumptions should be directly from the statement, not from our real life experiences or actual facts.
Example:Statement: Take a ferry or a boat instead of a bus to reach the Willington Islands faster.
Assumptions:
(I) The islands being in remote location are not easily accessible.
(II) Ferries and boats are available to travel to Willington Island..
Answer. Assumption I is not implicit, even if based on your real life experiences.
In statement, it is clearly stated that ferry or boat service save time to reach island, that means they are available to travel to Willington island. So II is implicit.
2. Assumptions should not be ambiguous.
Statement: An advertisement in the newspaper - 'Learn C++ course to get a highly paid job'.Assumptions:
(I) All those who learn C++ get highly paid jobs.
(II) Only a foreign language can get someone a high paying job.
Answer:The word 'all' makes the assumption I ambiguous. Similarly word 'only' makes assumption II ambiguous. So, both assumption are not true as per the statement so they are not implicit.
3. Words such as 'all', 'every', 'each', 'only', etc. in Assumption
Example1 : Based on the Statement which of the following Assumptions are implicit.Statement: Blast happened at the XYZ Cement factory last week was contributed by unskilled labours .Assumptions:
1.All labours of the factory is unskilled.
2.Only few labours are unskilled.
Answer. It is certain that factory has unskilled labours. But it doesn’t imply that ALL labours are unskilled. Statement doesn’t reveal that how many or how much unskilled labours are there. So,both assumptions are not implicit. Here the words ‘All’ and ‘Only’ makes the assumption ambiguous.
Example 2 : Based on the Statement which of the following Assumptions are implicit
Statement :Bangalore metro train service income mainly depends on the techies working in various MNCs.
Assumptions:
1. Every passenger of Bangalore metro train service is a techie working in an MNC.
2. Each and every Techie uses Bangalore metro train service for daily commute.
3. Most of the passengers of Bangalore metro train service are techies working in various MNCs.
Answer: From the statement it is clear that majority of passengers are techies. But it doesn’t imply that Every passenger is a Techy or each and every techie uses metro service.
So, Assumptions 1&2 are not implicit, and 3 is implicit.
Sunday, 11 June 2023
Reasoning Puzzles for Bank,PSC,RRB,UPSC and other compettitive exams
Reasoning Puzzles
Types of Reasoning puzzles based on number of variables
- Two variable puzzles
- Three Variable Puzzles
Two Variable puzzle Example
Make a table as follows
- P is not from Chennai.
- V is neither from Surat nor from Bengaluru.
- Either X or T is from Delhi.
- Y is from Mumbai.
- R is not from Bengaluru.
- V is neither from Pune nor from Chennai.
- Z is either from Surat or Bengaluru.
- T is not from Chennai.
- R is neither from Pune nor from Chennai.

Final result will be as follows.
Three Variable puzzle Example
Ajay decorated his house by coordinating orange and three other colour for walls, carpet and curtains of four rooms.From the in formation given below , determine the colour of carpet , walls and curtains for each room and answer the following questions.
- i. Yellow was the only colour used in all the four rooms.It was at least once for walls, carpets and curtains.
- ii. Three different colours were used in each room but only the dining room and the bedroom were decorated in the same three colours
- iii. The same colour was choosen for the curtains in the bedroom, the carpet in the living room and walls in the dining room.That colour was not used at all in the study room.
- iv. The only room with both green and grey in its colour scheme had carpet of the same colour as in the dining room.
- v. Grey was the only colour used exactly twice- both times for curtains.
- vi. The study room walls were painted the same colour as the living room walls
- v. Grey was the only colour used exactly twice- both times for curtains.
1.Which of the following room has orange curtains and green
walls ?
a) Dining room
b) Living room
c) Bedroom
d) Study room
e) None of these
2.Which of the rooms have green carpets?
a) Dining room and bedroom
b) Study room and living room
c) Living room and dining room
d) Study room and dining room
e) None of these
3.Which room did not use grey colour at all?
a) Dining room
b) Cannot say
c) Study room
d) Living room
e) None of these
4.The dining room has__ curtains.
a) Green
b) Yellow
c) Orange
d) Grey
e) None of these
5.Yellow-Green-orange colour combination
is used in which room?
a) Dining room
b) Bed room
c) Study room
d) Living room
e) Dining room and bed room
6.Orange is used how many times?
a) Two
b) Three
c) Four
d) Five
e) None of these
From above statement it is evident that two rooms have grey curtain and grey is used exactly two times. So all other chances of grey is striked off.
Statement iii. The same colour was chosen for the curtains
in the bedroom, the carpet in the living room and walls in the dining room. That
colour was not used at all in the study room.
From the above statement color used for curtains in the
bedroom, the carpet in the living room and walls in the dining room is not grey
or yellow, because grey is used twice only.
In statement ii. It is given that only the dining room and the bedroom were
decorated in the same three colours .From above grey is not used in bedroom so
in dining room also.
So first two rows will be either living or study room. Last
two rows will be either dining or bedroom.
From this we can infer that study room walls and living room walls are painted in yellow. Because green –grey combination is used once and orange in not present in either of living or study room .
In statement I Three different colours were used in each
room, so in first row strike off yellow from carpet column . and in second
column strike off yellow from carpet column.
In statement iii. The same colour was chosen for the curtains in the bedroom, the carpet in the living room and walls in the dining room. That colour was not used at all in the study room.
From above table curtains in the bedroom is - yellow/green/orange
carpet in the living is -green/orange Wall in dining room is -yellow/green/orange . So mentioned color is either green/orange. Strike off yellow from bedroom curtain and dining room wall .let third row be dining and fourth row be bed room .
From statement ii. Three different colours were used in each room , Dining room carpet will be orange.
but only the dining room and the bedroom were decorated in the same three colours.
Bed room curtain – green/orange
Carpet in living room – green/orange
Wall in Dining room –orange
From above bed room curtain is orange.
And from second part of statement iii . this color(orange ) was not used at all in the study room . There for first row is study room and second row is living room .
Since three different colors where used ,strike off other
oranges from Bed room.
Tuesday, 6 June 2023
Alphabet Test
Alphabet Test for competitive exams
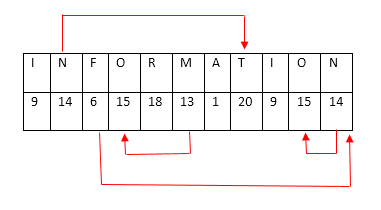
Alphabet test analyze your mental ability to identify the position of letters in English alphabets and their applications.Alphabet Test can be of three type.
- Find out letter with reference to the position of another letter.
- Arrangement of words in alphabetic/ dictionary order.
- Number of letters in a word ", which have as many letters between them in the word as in the alphabet.
- Find out missing letter/combinations of letters in a series.
- How many meaningful word can be formed from the given word.
Alphabet Test Examples:
Alphabet Test Type1:Find out letter with reference to the position of another letter1.In English Alphabet Which letter is the eighth letter to the right of the letter and which is tenth letter to the left of the last but one letter of the alphabet?
- last but one letter of the alphabet = Y
- tenth letter to the left of the last but one letter of the alphabet=tenth letter to the left of Y=O
- eighth letter to the right of the letter and which is tenth letter to the left of the last but one letter of the alphabet=eighth letter to the right of O = W
Alphabet Test Type 2:Arrangement of words in alphabetic/ dictionary order
1.Sort the following words into alphabetical order and mark the last one.i) Actuate
iii) Acquit
iv) Achieve
Ans: Option (i) .Since First letters of all words are same ,take the second letter. But, second letters are also same. So take third letters t,c,c,c. Here it is clear that 't' comes last.
Alphabet Test Type 3:Number of letters in a word ", which have as many letters between them in the word as in the alphabet.
iii) 2
iv) more than 4
Similarly F&N, M&O,N&O form a pair.
Alphabet Test Type 4:Find out missing letter/combinations of letters in a series.
i). CBT
ii). ABR
iii). BCT
iv). RBB
i) E
first letter A , last letter Z, similarly 2nd last letter Y with 2nd letter B
,3rd letter C with 3rd last letter X, 4th last letter W with 4th letter D
and so on....
Therefore the missing letter is X
Alphabet Test Type 5:How many meaningful word can be formed from the given word.
Sunday, 4 June 2023
Analogy Questions For competitive exams
Analogy
The word ANALOGY has been derived from two words. ANA means ”Relation” and "LOGUS" means Knowledge . The word literally means a- similar feature, condition, states etc.
- a process of reasoning based on ‘’similar feature”, ”a common feature” or ”Correspondence”
Analogy is an important section of General Intelligence because
it is the section through which examiners test the candidate’s ability to compare and establish proper
relationship among the given items on the basis of certain similarity .
How to Solve Analogy Questions for exams
In Analogy questions ,a particular relationship is given and similar relationship has to be identified from the given alternatives.
Analogy questions can be categorized into two types.
- Semantic Analogy
- Symbolic /Number Analogy
Semantic Analogy
The term "semantic" refers to what language means, or the study of meaning and logic. The relationship between two given words is established and then applied to the other pair of words.
Example:1.COURT:JUSTICE::HOSPITAL: ?
i) Medicne
ii) Operation
iii) Treatment
iv) Doctor
Ans (iii)Justice is given in court, treatment is given in hospital
2.CLOCK:TIME
ii) People:Way
iii) Book:Knowledge
iv) Map:Place
i) Hut:Mansion
ii)Giant:Dwarf
iii)Horse:Foal
iv)Ant:Elephant
Ans: (iii)Young tree is sapling, young Horse is a foal.
Symbolic /Number Analogy
In this type of analogy the
relationship between the value of alphabetical letters or principle and rules
of mathematical equation are identified. Then applied to the other set to
obtain the required set of letters .
1) JILK:KLIJ::MNPQ?
ii). MPQN
iii). QPNM
iv). PNMQ
Ans : (iii) order of letters are reversed.
2)Which number will come in the place of question mark ?
36 : 18 : : 72 : ?
ii). 134
iii). 94
iv). 14
Ans :iv, The second number is the product of digits of the first number.
36:18::72:14 ∣3×6∣∣7×2∣
Friday, 2 June 2023
Geometric Progression :Important formulas
Geometric Progression
Geometric
Progression (GP) is a sequence, in which next term in the sequence is obtained
by multiplying the previous term by a fixed number, and the fixed number is
called the Common Ratio.
Example: 5,15,45,135 … is a GP with first term 5 and common
difference 3
General form of Geometric Progression
A
geometric sequence or a progression is one in which the ratio between two
consecutive terms is constant. This ratio is known as the common ratio denoted
by ‘r’, where r ≠ 0. The elements of the
sequence be denoted by:
a, ar, ar2, ar3, … , arn-1
common
ratio ‘r’= successive
term/preceding term =a2/a1 = a3/a2 = = an/an-1
Types of Geometric Progression
Geometric
progression can be classified as
- Finite
Geometric Progression (Finite GP)
- Infinite
Geometric Progression (Infinite GP)
Finite G.P. is a sequence that contains finite terms in a sequence and can be written as a, ar, ar2, ar3,……arn-1, arn.
Example
:2,4,6,8,10…….98,100
Infinite G.P. is a sequence that contains infinite terms and can be written as a, ar, ar2, ar3,……arn-1, arn……..
Nth Term of a Geometric Progression
nth term of a G.P whose first term is ‘a’ and number of terms in sequence is ‘n’ can be written as
an = arn-1
nth term of a G.P if last term is known.
an = l/rn-1
where, l is the last term
Sum of the First n Terms of a finite
Geometric Progression
Sum of the
First n Terms of a Geometric Sequence is given by:
Sn = a(1 – rn)/(1 – r), if r < 1
Sn = a(rn -1)/(r – 1), if r > 1
Sum of the First n Terms of a infinite
Geometric Progression
The
sum of infinite geometric progression can only be defined at the range of |r|
< 1.
S = a(1 – rn)/(1 – r)
S = (a – arn)/(1 – r)
S = a/(1 – r) – arn/(1 – r)
For n -> ∞, the quantity (arn) / (1 – r) → 0 for |r|
< 1,
Thus,
S∞= a/(1-r), where |r| < 1
IBPS Clerk Prelim model question paper pdf download
IBPS Clerk Preliminary model Paper pdf ebook IBPS has already released Clerk Notification for CWE XIII 2023. The online examination (P...

-
Here we are sharing some useful shortcut tricks for finding square,cube,square root and cube root which will be helpful in competitive exam...
-
Here you can find important formulas and time saving shortcut tricks and methods for simple interest and compound interest questions for va...
-
Geometric Progression Geometric Progression (GP) is a sequence, in which next term in the sequence is obtained by multiplying the previous...