Coding and Decoding Questions with Answers
Coding and decoding is an important reasoning topic for most of the government competitive exams like IBPS,SSc CGL,SSC CHSL,RRB,RBI,SBI written examinations. In this page you can find Coding and Decoding important short cuts and tricks as well as coding and decoding practice questions with solution. We have tried to cover important coding and decoding test questions that are asked in SSC,UPSC,IBPS,RRB exams. We have used easiest shortcut methods and tricks for solving coding and decoding questions .
Definition of Coding and Decoding
Coding:Coding is the process of converting a piece of information into another form of representation through symbols.
Decoding:It is the reverse process of coding by which coded data is converted back into original information.
Classification of Coding and Decoding
- Letter Coding
- Number Coding
- Substitution Coding
- Deciphering Coding
- Symbol Coding
Letter Coding and Decoding
In this type of coding letters of a word are replaced by certain other letter according to a specific pattern/rule to form a code.To solve these kind of questions you must know position of alphabets from both ends.

Position of letters can also be remembered by the formula “EJOTY”.

E is 5th from left ,j is 10th from left and so on..
You can also use another formula “BGLQV” for getting position of letters in reverse order .

B is 25th from right ,G is 20th from right and so on..
Position of a letter from left=27- position of letter from right.
Example1:If in a code ‘MASTER’ is written as ‘SAMRET’, then how ‘PEOPLE’ be written in the same code?
- 1.PEOLEP
- 2.PLEOPE
- 3.EPPOEL
- 4.OEPELP
Answer with explanation .( 4)In this position of letters are changed according to a specific pattern
- PLQXMH
- PLQZNI
- QMNYNJ
- OLQXWG
Answer with explanation. (1)Here each letter is replaced by some other letter according to a specific pattern.Each letter is replaced by third letter right of that letter.

Similarly

Example3:In a code BOXER is written as AQWGQ then VISIT is written as –
- UKRKU
- UKRKS
- WKRKU
- WKRKS
Answer with explanation:(2)

Similarly
Example4:If CEG is written as TSR and FHJ is written as QPO then IKM is written as-
- NOP
- PON
- MLK
- NML
Answer With explanation:(4)


Example 5:In a certain code PLAN written as QBMS then RAIN is written as –
- UBJQ
- UBJR
- QJBU
- QBJU
Answer with explanation: (3)
Number Coding
In this type of coding numerical values are assigned to a word or alphabets according to predefined pattern.
Examle1: If ORAL is coded as 3196, then how can NUMBER be coded?
- 954253
- 592435
- 952435
- 235679
Answer with explanation:(3)
Substitution coding
In this type of coding codes are assigned by the substitution method where in an artificial alternative is assigned to a given word and candidates are required to decipher the coding pattern to substitute the given word?
Example: If in a code language 'white' is called 'black', 'black' is called 'yellow', 'yellow' is called 'blue', 'blue' is called 'red' ,'red' is called 'green', then what is the color of human blood.
- yellow
- blue
- red
- green
Answer with explanation:(4) As, we know that colour of human blood is red ,here 'red' means 'green'.Hence, colour of human blood is 'green'.
Deciphering Coding
In these type of questions, a message bearing a common code for given word/numeral .Candidates are required to identify the code from the common property of word/numerals and decipher the given codes with best alternatives.
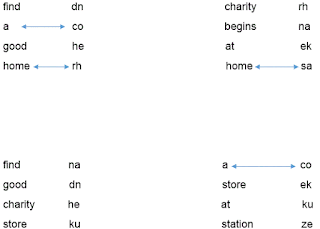
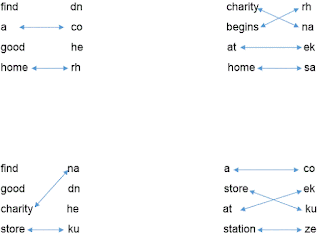
Example:In a certain code language “find a good home” is written as “dn co he rh”, “charity begins at home” is written as “rh na ek sa”, “find good charity store” is written as “na dn he ku” and “a store at station” is written as “co ek ku ze”. (All codes are two-letter codes only).
Solution:Arrange each sentence and their corresponding code as shown below.
You will obtain four sets as above.Now consider the word 'find'. You can see the word 'find' in set 1 and set 3. You can also see the word 'good' is common to set 1 and set 3.If there are more than one common word in two set you cannot reach a conclusion.Now go for next word 'a'.The word 'a' is common to set 1 and set 4.There is only one common term between set 1 and set 4.Thus you can conclude that code of 'a' is 'co'. Draw a matching line connecting 'a' and 'co'. This will help you avoid confusion while making the right answer.From set 1 and set 2 you will get code of the word 'home' as 'rh'. Draw a matching line connecting the word and corresponding code.
Continue above procedure for each word.Within 5-6 steps you can solve complete set of codes.You will get an arrangement like this.
Note that code for the words 'find' and 'good' is either 'dn' or 'he'.
Symbol Coding
In this type of coding a set of symbol is assigned to a group of letters.Candidates are require to identify the relation between the symbol and decipher the pattern of coding and choose the best alternative.
Example: Ina certain code language ,'SAFER' is written as '5@3#2' and 'RIDE' is written as '2&%#',how would 'FEDS' be written in that code language?
- 3#&5
- 3@%5
- 3#%5
- 3#%2
Answer with explanation:(3)Here each letter is replaced by a symbol.Order of word and code is same.No shuffling or position pattern is applied.
For getting coding decoding
questions with answers pdf ,kindly like and share this article and contact us through contact form given below.